MCQ questions on Elasticity
1. Young’s modulus is the property of
(a) Gas, (b) Liquid, (c) solid, (d) both solid and liquid
option c
2. Young’s modulus has the dimension of
(a) Force, (b) Stress, (c) Strain, (d) None of these
option b
3. The reciprocal of bulk modulus is called
(a) Modulus of elasticity, (b) Compressibility, (c) Modulus of rigidity, (d) Viscosity
option b
4. Magnitude of elasticity of perfectly elastic body is
(a) Infinity, (b) Zero, (c) 1, (d) None of these
option a
5. S.I unit of Poisson’s ratio is
(a) Nm-2 , (b) Nm, (c) N, (d) Unitless
option d
Short answer type questions on Elasticity
1. What is Hooke’s law?
Hooke’s law: Within elastic limit, stress is proportional to strain.
Therefore, Stress \propto Strain
\frac{Stress}{Strain}=Constant
2. Why strain is more fundamental than stress?
Strain is a direct measure of the deformation of a material, while stress is a measure of the force causing the deformation. In other words, strain is a more direct measure of the physical response of a material to externa
3. Which is more elastic rubber or steel? Explain
Steel is more elastic than rubber. The elastic property of a material is defined as the force required to deform a body. To get same amount of deformation, greater force is required to steel than rubber. So, steel has greater elastic property.
4. Draw the stress versus strain graph of an elastic body.
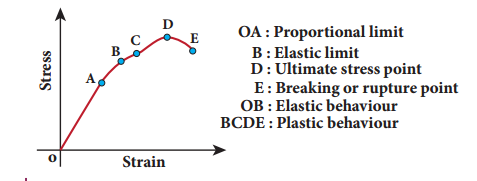
5. Define stress, strain, Young’s modulus, Bulk modulus, Modulus of rigidity and Poisson’s ratio.
Stress: Restoring force per unit area is called stress.
Strain=\frac{Force(F)}{Area(A)}
Strain: Strain gives the fractional change in the size of an object.
Strain = \frac{Change \hspace{0.2cm} in \hspace{0.2cm} size}{Original \hspace{0.2cm}size}
Young’s modulus (Y): Within elastic limit, the ratio of longitudinal stress to longitudinal strain is called Young’s modulus.
Y=\frac{longitudinal \hspace{0.2cm} stress}{longitudinal \hspace{0.2cm} strain}
Bulk modulus (K): Within elastic limit, the ratio of volume stress to volume strain is called Bulk modulus.
K=\frac{volume \hspace{0.2cm} stress}{volume \hspace{0.2cm} strain}
Rigidity modulus (n): Within elastic limit, the ratio of shearing stress to shearing strain is called modulus of rigidity.
n=\frac{shearing \hspace{0.2cm} stress}{shearing \hspace{0.2cm} strain}
Poisson’s ratio: Within elastic limit, the ratio of lateral strain to longitudinal strain is called Poisson’s ratio.
Poisson's \hspace{0.2cm} ratio=\frac{lateral \hspace{0.2cm} strain}{longitudinal \hspace{0.2cm} strain}