Multiple choice questions on ELECTROSTATICS for engineering, board exams, NEET JEE
Some important questions are discussed on electrostatics for all engineering branches and other board exams including NEET, JEE, WBJEE, KVPY exams. The main topics of this chapter are coulomb’s law, electric field, electric flux, electric potential, potential energy and Gauss’s law. These questions will help students of all engineering branches of first year engineering course to get clear understanding on this topic of Physics.
MCQ multiple choice questions with answers on electrostatics for engineering and board exams
1. The unit of electric field
a. V.m-1
b. V.m2
c. V.m
d. V.m-2
option c
2. The number of electrons corresponding to 1 Coulomb of charge
a. 6.25✕1017
b. 6.25✕1018
c. 6.25✕1019
d. 1.6✕1019
option b
Number of electrons = 1/ charge of electron = 1/(1.6✕10-19 )=6.25✕1018
3. On moving a charge of 20 coulomb by 2 cm, 2 J of work is done, then the potential difference between the points is
a. 0.1 V
b. 8 V
c. 2 V
d. 0.5 V
option a
Work done = charge ✕ potential difference
W=qV
V = W/q= 2J/20C = 0.1 V
4. The electric field at distance r from the center of a charged hollow sphere of radius R is (r>R)
a. E∝ r
b. E∝ r2
c. E∝ 1/r
d. E∝ 1/r2
option d
5. The electric flux linked with a surface become maximum if the angle between the field lines and the normal to the surface is
a. 0°
b. 45°
c. 90°
d. 180°
option a
flux = E.A =EACosθ
So, when θ is 0, flux is maximum
6. The electric flux is a ——– quantity
a. Scalar
b. Vector
c. Tensor
d. None of the above
option a
7. 1 volt = ——- statvolt
a. 1/100
b. 1/300
c. 100
d. 300
option b
8. A charge Q is enclosed by a gaussian spherical surface of radius R. If the radius is doubled, then the outward electric flux will Increase
a. four times
b. be reduced to half
c. remain the same
d. be doubled
option C
9. Two-point charges +8q and -2q are located at x=0 and x=L respectively. The location of a point on the x-axis at which the net electric field due to these two-point charges is zero is
a. L/4
b. 2L
c. 4L
d. 8L
option b
10. Two points P and Q are maintained at the potentials of 10 V and – 4 V, respectively. The work done in moving 100 electrons from P to Q is
a. 9.60 × 10-17 J
b. -2.24 × 10-16 J
c. 2.24 × 10-16 J
d. -9.60 × 10-17 J
option b
Short answer type questions of electrostatics – PHYsics for engineering students of first year
1. State Coulomb’s law.
The force on a point charge q2 exerted by another point charge q1 is
F21=Kq1q2/(r12)2 in the direction of r12vector
Where r12is the vector from q1to q2
2. What is the dimension of permittivity?
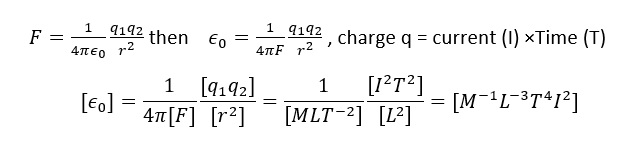
3. Define electric field.
The electric field at a point is defined as the force per unit charge.
So, if a charge q experiences a force F in an electric field E, then
E=F/q
So, the unit of electric field is N.m-1 or V.m and it is a vector quantity
4. The electric field lines never intersect. Justify this statement
Electric field lines never intersect each other. If two lines intersect at any point, then there will be two tangent along the two field lines. So, there will be two directions of electric field at the same point. Hence, two electric field line can never intersect.
5. What do you mean by electric flux?
The number of field lines passing through a given area kept normal to the electric field lines is called electric flux.
The electric flux Φ through an area A in an electric field E is
Φ=E.A
E and A are vector quantity, but flux Φ is a scalar quantity.
The unit of electric flux is N.m2.C-1
6. State Gauss’s law in electrostatics.
7. Define electrostatic potential.
The electric potential at a point is defined as the work done in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to than point by an external force.
Electric potential is a scalar quantity.
8. What is the potential at a distance r from a point charge q?
The potential at a distance r from a point charge q is
V(r) = q/4Πε0r
9. Find the electric field due to a solid charged sphere.